Abstracts of Evaluation Studies
of Microhydrin®
A Functional Silicate Nanocolloid |
Clinton H. Howard and Kimberly Lloyd
Revised January, 2000
RBC Life Sciences is conducting an ongoing series of laboratory and clinical studies designed to evaluate the nutritional characteristics and benefits of Microhydrin (250 mg per capsule) as a mineral antioxidant. The following is a brief summary of the results of studies completed as of January 2000.
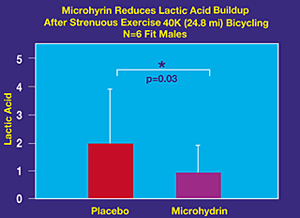
Microhydrin® Effectively Lowered Blood Lactic Acid
Levels During Strenuous Exercise
The Exercise Physiology Department of the University of North Texas Health Science Center at Fort Worth, Texas conducted a double blind, placebo controlled crossover study in 6 male cyclists for blood lactic acid (lactate) clearance during a 40K (24.8 mi) timed bicycle ride at maximum speed. Subjects received 4 capsules of Microhydrin or placebo daily taking one in the morning, two at noon and one in the evening during the week prior to testing and during the week of testing. Subjects refrained from all other non-prescribed supplements during the testing period. Additionally, subjects took 2 capsules with water 30 min. before the start of exercise. Blood lactate levels was measured before and 5 min. after each exercise session. Microhydrin significantly decreased blood lactic acid (lactate) levels as compared to placebo during strenuous exercise (p = 0.03). (Published data Journal of Medical Foods, 1999 Vol 3 No.4 p151-159 Peter Raven Ph.D. 1999 & Wendy Wasmund, B.S. University of North Texas Health Science Center at Fort Worth, 1999.)
Lactic acid accumulates during strenuous or prolonged exercise. It is a common problem for athletes, people who work out, play sports or do physical exercise for an extended time.
The decreased lactic acid (lactate) levels immediately after strenuous exercise is another indicator of the ability of Microhydrin to help in providing a direct energy source (ATP production) to cellular function. An ergogenic energy function is when a substance enhances biochemical energy without introducing additional carbohydrates or calories to the diet.
Microhydrin in Intra and Extra Cellular Hydration
A double blind placebo controlled pilot study was conducted using the RJL Bioelectrical Impedance Analyzer that measures hydration of the body based on nutritional status developed by R. J. Liedtke. Seven subjects received 4 capsules of Microhydrin per day for two weeks and were crossed over receiving 4 capsules per day of a placebo (rice bran flour). Averaged values showed increased intracellular and extracellular hydration due to the consumption of Microhydrin as compared to the placebo group.
The increase observed in Extracellular Water values were statistically significant (p < 0.05) when consuming Microhydrin as compared to taking the placebo. (Unpublished data Gary Osborn R.Ph. & Heriberto Salinas, MD Texas Institute of Functional Medicines, 1999)
Body Cell Mass (BCM) and Intracellular Water (ICW) are assessments of intracellular volume and water inside the cell, respectively. Extracellular Body Water, water that bathes the cells, also showed increased volume. Intracellular water makes up approximately 60% of the total body water of healthy adults. Intracellular water, as an indicator of cell integrity, is found to be higher in babies but decreases as adults age or lose body cell mass. Healthy tissue cells hold water within the cells and have higher anabolic (building up) function rather than catabolic (breaking down) function.< P>
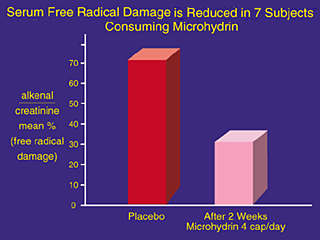
Microhydrin Protection Against Oxidative Stress
A double blind placebo controlled crossover pilot study was conducted on 7 subjects who received 4 capsules/day of Microhydrin for two weeks, and received 4 capsules/day of a placebo for two weeks. Urine alkenal/creatinine ratios were measured. During Microhydrin supplementation, a 43% increase in free radical protection was observed as compared to the placebo group. Microhydrin was observed in this study to protect against serum alkenals. Alkenals are the oxidative products of serum lipid peroxides occurring from free radical attacks on cellular lipid membranes and lipoproteins. They are indicators of free radical damage in the body associated with a higher risk of age related diseases. (Unpublished data Gary Osborn R.Ph. & Heriberto Salinas, MD Texas Institute of Functional Medicines, 1999)
Evaluation of Microhydrin in the Production of NADH in Vitro
ATP production, the principal source of energy in the mitochondria, depends on the production of NADH. Reduced hydrogen, generated by the Kreb’s Cycle, is carried by NADH into the mitochondria for the electron transport chain reactions that will ultimately create a molecule of water and ATP.
Hydrogen is one of the most important elements donating an electron, an electron pair or its proton to reduction/oxidation reactions of numerous enzymes and intermediates within the cell’s metabolic pathways. In vitro assays measured the direct conversion of NAD+ to
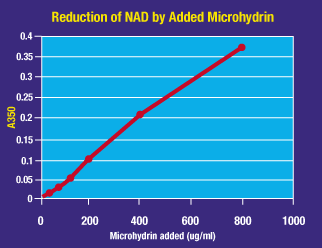
NADH by the addition of Microhydrin. The sequential addition of increasing concentrations of Microhydrin to NAD+ showed a linear increase in NADH production as measured by its absorption at 350 nm. (Unpublished data Joe McCord, Ph.D University of Colorado Health Sciences Center, 1998).
Next